本文对ResNet源码(Pytorch)进行解读。许多网络结构的改进是在其基础上做的,因此有必要仔细理解下。
注:为了增强代码的易读性,本文所展示的代码基于2021年3月11日的torchvision代码删减得到的,因此和源码并不完全一致,需要的读者可以前往查看torchvision的ResNet源码。
首先定义了预训练模型下载地址,封装了3x3和1x1的卷积核
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
model_urls = {
'resnet18': 'https://download.pytorch.org/models/resnet18-5c106cde.pth',
...
'resnext50_32x4d': 'https://download.pytorch.org/models/resnext50_32x4d-7cdf4587.pth',
...
'wide_resnet50_2': 'https://download.pytorch.org/models/wide_resnet50_2-95faca4d.pth',
...
}
# basic 3x3 conv wrapper
def conv3x3(in_planes: int, out_planes: int, stride: int = 1, groups: int = 1, dilation: int = 1) -> nn.Conv2d:
"""3x3 convolution with padding"""
return nn.Conv2d(in_planes, out_planes, kernel_size=3, stride=stride,
padding=dilation, groups=groups, bias=False, dilation=dilation)
# basic 1x1 conv wrapper
def conv1x1(in_planes: int, out_planes: int, stride: int = 1) -> nn.Conv2d:
"""1x1 convolution"""
return nn.Conv2d(in_planes, out_planes, kernel_size=1, stride=stride, bias=False)
接下来正式开始网络的定义。
两种基本模块
ResNet主要是由两种基本模块堆叠而成的:BasicBlock和BottleNeck,模块结构定义如下
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
# Naive residual block for Renset18/34
class BasicBlock(nn.Module):
expansion = 1
def __init__(
self,
inplanes,
planes,
stride=1,
downsample=None,
):
super(BasicBlock, self).__init__()
# Both self.conv1 and self.downsample layers downsample the input when stride != 1
self.conv1 = conv3x3(inplanes, planes, stride)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.conv2 = conv3x3(planes, planes)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes)
self.downsample = downsample
self.stride = stride
def forward(self, x):
identity = x
# Conv + BatchNorm + RelU
out = self.conv1(x)
out = self.bn1(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.conv2(out)
out = self.bn2(out)
if self.downsample is not None:
identity = self.downsample(x)
out += identity
out = self.relu(out)
return out
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
# BottleNeck Residual block for Renset50/101/152
class Bottleneck(nn.Module):
# Bottleneck in torchvision places the stride for downsampling at 3x3 convolution(self.conv2)
# while original implementation places the stride at the first 1x1 convolution(self.conv1)
# according to "Deep residual learning for image recognition"https://arxiv.org/abs/1512.03385.
# This variant is also known as ResNet V1.5 and improves accuracy according to
# https://ngc.nvidia.com/catalog/model-scripts/nvidia:resnet_50_v1_5_for_pytorch.
expansion = 4
def __init__(
self,
inplanes,
planes,
stride=1,
downsample=None
):
super(Bottleneck, self).__init__()
# Both self.conv2 and self.downsample layers downsample the input when stride != 1
self.conv1 = conv1x1(inplanes, planes)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes)
self.conv2 = conv3x3(planes, planes, stride)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes)
self.conv3 = conv1x1(planes, planes * self.expansion)
self.bn3 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes * self.expansion)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.downsample = downsample
self.stride = stride
def forward(self, x):
identity = x
out = self.conv1(x)
out = self.bn1(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.conv2(out)
out = self.bn2(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.conv3(out)
out = self.bn3(out)
if self.downsample is not None:
identity = self.downsample(x)
out += identity
out = self.relu(out)
return out
两个模块的实现均比较直白,画出示意图如下图所示。
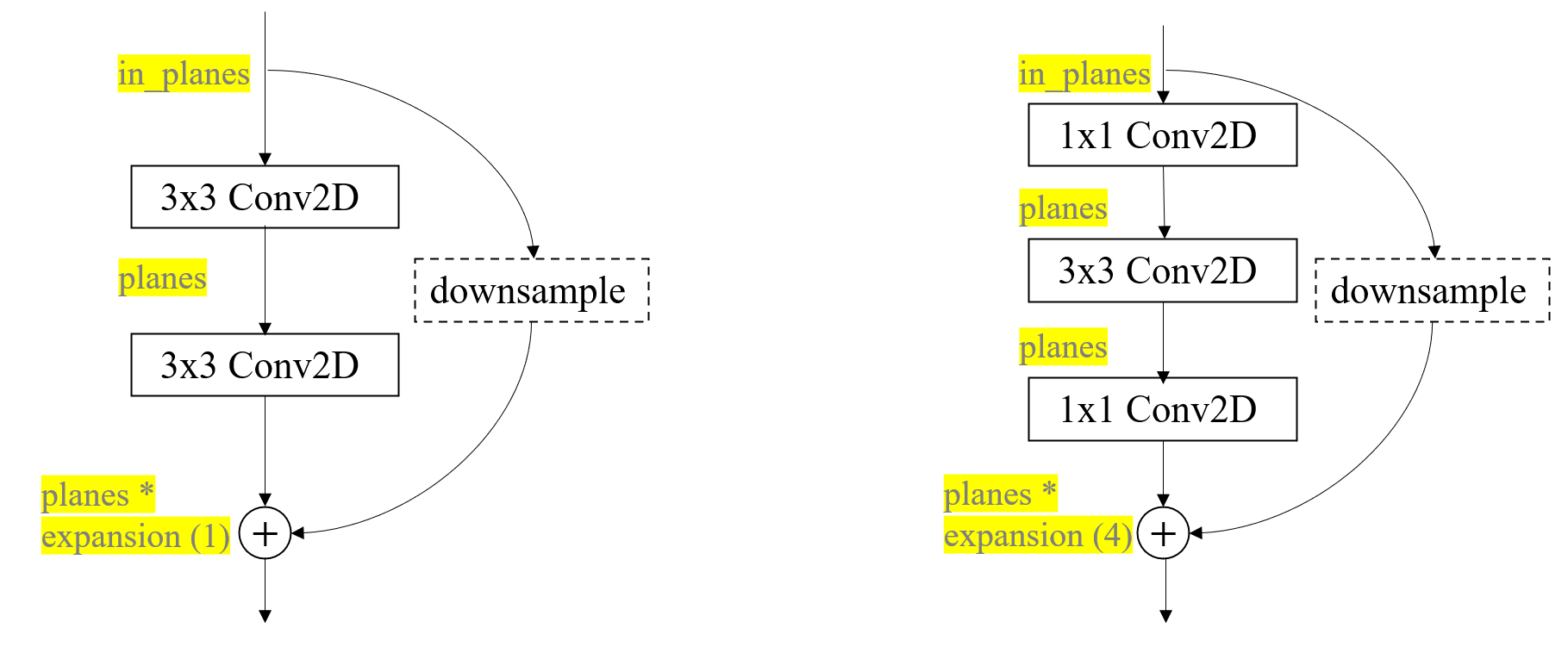
可以总结为,两个block类型都是输入一个inplanes维的特征图,输出一个planes*block.expansion维的特征图(注意而不是planes。BasicBlock的expansion=1)。
downsample操作是为了对shortcut支路进行大小或维度上的调整,以使得该路输出与residual路支路输出保持维度一致,以执行相加操作。downsample的具体定义会在下文构建整个ResNet网络时提到。
ResNet网络整体结构
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
class ResNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(
self,
block,
layers,
num_classes=1000,
zero_init_residual=False
):
super(ResNet, self).__init__()
self.inplanes = 64
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(3, self.inplanes, kernel_size=7, stride=2, padding=3,
bias=False)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(self.inplanes)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.maxpool = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1)
self.layer1 = self._make_layer(block, 64, layers[0])
self.layer2 = self._make_layer(block, 128, layers[1], stride=2)
self.layer3 = self._make_layer(block, 256, layers[2], stride=2)
self.layer4 = self._make_layer(block, 512, layers[3], stride=2)
self.avgpool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((1, 1))
self.fc = nn.Linear(512 * block.expansion, num_classes)
for m in self.modules():
if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
nn.init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight, mode='fan_out', nonlinearity='relu')
elif isinstance(m, (nn.BatchNorm2d)):
nn.init.constant_(m.weight, 1)
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
# Zero-initialize the last BN in each residual branch,
# so that the residual branch starts with zeros, and each residual block behaves like an identity.
# This improves the model by 0.2~0.3% according to https://arxiv.org/abs/1706.02677
if zero_init_residual:
for m in self.modules():
if isinstance(m, Bottleneck):
nn.init.constant_(m.bn3.weight, 0) # type: ignore[arg-type]
elif isinstance(m, BasicBlock):
nn.init.constant_(m.bn2.weight, 0) # type: ignore[arg-type]
# construct layer/stage conv2_x,conv3_x,conv4_x,conv5_x
def _make_layer(self, block, planes, blocks, stride=1):
downsample = None
# when need to downsample
if stride != 1 or self.inplanes != planes * block.expansion:
downsample = nn.Sequential(
conv1x1(self.inplanes, planes * block.expansion, stride),
nn.BatchNorm2d(planes * block.expansion),
)
layers = []
layers.append(block(self.inplanes, planes, stride, downsample))
# inplanes are expanded / self.inplanes is freshed for next block
self.inplanes = planes * block.expansion
for _ in range(1, blocks):
layers.append(block(self.inplanes, planes))
return nn.Sequential(*layers)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv1(x)
x = self.bn1(x)
x = self.relu(x)
x = self.maxpool(x)
x = self.layer1(x)
x = self.layer2(x)
x = self.layer3(x)
x = self.layer4(x)
x = self.avgpool(x)
# For `torch.flatten`, this blog may help: https://blog.csdn.net/GhostintheCode/article/details/102530451
# so `x = torch.flatten(x, 1)` is equivalent to `x = x.view(x.size(0), -1)` in the previous versions, where `x.size(0)` is the batch_size
x = torch.flatten(x, 1)
x = self.fc(x)
return x
可以看到,首先一个7 x 7的卷积作用在输入的3维图片上,并输入一个64维的特征图(64也就为self.inplanes的初始值),通过BatchNorm层,ReLU层,MaxPool层;然后经过4层layer,这4层layer通过_make_layer()函数构建,是上述两种模块的堆叠,下文将详细介绍;最后经过一个AveragePooling层,再经过一个fc层得到分类输出。
另外在网络搭建起来后,还对模型的参数(Conv2d、BatchNorm2d、last BN)进行了初始化。
_make_layer()函数是理解网络结构的关键。单独拎出来看一下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
def _make_layer(self, block, planes, blocks, stride=1):
downsample = None
if stride != 1 or self.inplanes != planes * block.expansion:
downsample = nn.Sequential(
conv1x1(self.inplanes, planes * block.expansion, stride),
nn.BatchNorm2d(planes * block.expansion),
)
layers = []
layers.append(block(self.inplanes, planes, stride, downsample))
self.inplanes = planes * block.expansion
for _ in range(1, blocks):
layers.append(block(self.inplanes, planes))
return nn.Sequential(*layers)
一个_make_layer()构建一个layer层,每一个layer层是上述两种模块的堆叠。输入参数中block代表该layer堆叠模块的类型,可选BasicBlock或者BottleNeck;blocks代表该layer中堆叠的block的数目;planes与该layer最终输出的维度数有关,注意最终输出的维度数=planes * block.expansion.
首先判断是否需要downsample操作。如前所述,downsample操作是为了对shortcut支路进行大小或维度上的调整,以使得该路输出与residual支路输出保持一致,保证可以执行相加操作。因此有两种情况需要对block的shortcut支路执行downsample操作:
stride != 1:需要对shortcut支路特征图进行大小上的调整。在整个代结构中,卷积的stride值都是默认为1的,在同样默认为1的padding作用下,得到的特征图大小将保持不变。但可以看到,layer2,layer3,layer4在构建时,指定了stride为2(只对该layer的第一个block生效),这将使得residual支路的输出特征图在大小上小于shortcut支路,因此需要对shortcut支路增加一个downsample支路,也做一下stride=2的卷积,保证两支路输出大小一致,即1
conv1x1(self.inplanes, planes * block.expansion, [stride=2])
self.inplanes != planes * block.expansion:需要对shortcut支路特征图进行维度数目上的调整。shortcut支路的输出维度为即为输入维度self.inplanes,而residual支路的输出维度为plane * block.expansion,二者可能不一致,也就是self.inplanes != planes * block.expansion,当该情况发生,对shortcut支路输出进行维度上的调整,从self.inplanes调整至planes * block.expansion,即1
conv1x1(self.inplanes, [planes * block.expansion], stride)
当一个layer包含多个block时,是通过向layers列表中依次加入每个block,来实现block的堆叠的。第一个block需要特殊处理,该block依据传入的self.inplanes, planes以及stride判断,可能含有downsample支路;这个block的输出维度是planes*block.expansion。紧接着便把self.inplanes更新为此值作为后续block的输入维度。后面的block的stride为默认值1,同时,由于输入为self.inplanes,输出为planes*block.expansion,而self.inplanes = planes * block.expansion,因此不会出现特征图大小或者尺寸不一致的情况,不可能出现downsample操作,就可以放心for循环加进列表啦。
ResNet实例化
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
def resnet18(pretrained=False, **kwargs):
"""Constructs a ResNet-18 model.
Args:
pretrained (bool): If True, returns a model pre-trained on ImageNet
"""
model = ResNet(BasicBlock, [2, 2, 2, 2], **kwargs)
if pretrained:
model.load_state_dict(model_zoo.load_url(model_urls['resnet18']))
return model
def resnet34(pretrained=False, **kwargs):
"""Constructs a ResNet-34 model.
Args:
pretrained (bool): If True, returns a model pre-trained on ImageNet
"""
model = ResNet(BasicBlock, [3, 4, 6, 3], **kwargs)
if pretrained:
model.load_state_dict(model_zoo.load_url(model_urls['resnet34']))
return model
def resnet50(pretrained=False, **kwargs):
"""Constructs a ResNet-50 model.
Args:
pretrained (bool): If True, returns a model pre-trained on ImageNet
"""
model = ResNet(Bottleneck, [3, 4, 6, 3], **kwargs)
if pretrained:
model.load_state_dict(model_zoo.load_url(model_urls['resnet50']))
return model
def resnet101(pretrained=False, **kwargs):
"""Constructs a ResNet-101 model.
Args:
pretrained (bool): If True, returns a model pre-trained on ImageNet
"""
model = ResNet(Bottleneck, [3, 4, 23, 3], **kwargs)
if pretrained:
model.load_state_dict(model_zoo.load_url(model_urls['resnet101']))
return model
def resnet152(pretrained=False, **kwargs):
"""Constructs a ResNet-152 model.
Args:
pretrained (bool): If True, returns a model pre-trained on ImageNet
"""
model = ResNet(Bottleneck, [3, 8, 36, 3], **kwargs)
if pretrained:
model.load_state_dict(model_zoo.load_url(model_urls['resnet152']))
return model
通过指定block的类别(如BasicBlock),四个layer依次堆叠的block数目(如[2, 2, 2, 2]),以及一些字典类型参数**kwargs,就可以实例化出一个ResNet模型啦。
完整代码
需要再次强调的是,本文所展示的代码基于2021年3月11日的torchvision代码删减得到的,因此和源码并不完全一致,需要的读者可以前往查看torchvision的ResNet源码。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
220
221
222
223
224
225
226
227
228
229
230
231
232
233
234
235
236
237
238
239
240
241
242
243
244
245
246
247
248
249
250
251
252
253
254
255
256
257
258
259
260
261
262
263
264
265
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.utils.model_zoo as model_zoo
__all__ = ['ResNet', 'resnet18', 'resnet34', 'resnet50', 'resnet101',
'resnet152', 'resnext50_32x4d', 'resnext101_32x8d',
'wide_resnet50_2', 'wide_resnet101_2']
model_urls = {
'resnet18': 'https://download.pytorch.org/models/resnet18-5c106cde.pth',
'resnet34': 'https://download.pytorch.org/models/resnet34-333f7ec4.pth',
'resnet50': 'https://download.pytorch.org/models/resnet50-19c8e357.pth',
'resnet101': 'https://download.pytorch.org/models/resnet101-5d3b4d8f.pth',
'resnet152': 'https://download.pytorch.org/models/resnet152-b121ed2d.pth',
'resnext50_32x4d': 'https://download.pytorch.org/models/resnext50_32x4d-7cdf4587.pth',
'resnext101_32x8d': 'https://download.pytorch.org/models/resnext101_32x8d-8ba56ff5.pth',
'wide_resnet50_2': 'https://download.pytorch.org/models/wide_resnet50_2-95faca4d.pth',
'wide_resnet101_2': 'https://download.pytorch.org/models/wide_resnet101_2-32ee1156.pth',
}
def conv3x3(in_planes: int, out_planes: int, stride: int = 1, groups: int = 1, dilation: int = 1) -> nn.Conv2d:
"""3x3 convolution with padding"""
return nn.Conv2d(in_planes, out_planes, kernel_size=3, stride=stride,
padding=dilation, groups=groups, bias=False, dilation=dilation)
def conv1x1(in_planes: int, out_planes: int, stride: int = 1) -> nn.Conv2d:
"""1x1 convolution"""
return nn.Conv2d(in_planes, out_planes, kernel_size=1, stride=stride, bias=False)
class BasicBlock(nn.Module):
expansion = 1
def __init__(
self,
inplanes,
planes,
stride=1,
downsample=None,
):
super(BasicBlock, self).__init__()
# Both self.conv1 and self.downsample layers downsample the input when stride != 1
self.conv1 = conv3x3(inplanes, planes, stride)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.conv2 = conv3x3(planes, planes)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes)
self.downsample = downsample
self.stride = stride
def forward(self, x):
identity = x
out = self.conv1(x)
out = self.bn1(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.conv2(out)
out = self.bn2(out)
if self.downsample is not None:
identity = self.downsample(x)
out += identity
out = self.relu(out)
return out
class Bottleneck(nn.Module):
# Bottleneck in torchvision places the stride for downsampling at 3x3 convolution(self.conv2)
# while original implementation places the stride at the first 1x1 convolution(self.conv1)
# according to "Deep residual learning for image recognition"https://arxiv.org/abs/1512.03385.
# This variant is also known as ResNet V1.5 and improves accuracy according to
# https://ngc.nvidia.com/catalog/model-scripts/nvidia:resnet_50_v1_5_for_pytorch.
expansion = 4
def __init__(
self,
inplanes,
planes,
stride=1,
downsample=None
):
super(Bottleneck, self).__init__()
# Both self.conv2 and self.downsample layers downsample the input when stride != 1
self.conv1 = conv1x1(inplanes, planes)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes)
self.conv2 = conv3x3(planes, planes, stride)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes)
self.conv3 = conv1x1(planes, planes * self.expansion)
self.bn3 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes * self.expansion)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.downsample = downsample
self.stride = stride
def forward(self, x):
identity = x
out = self.conv1(x)
out = self.bn1(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.conv2(out)
out = self.bn2(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.conv3(out)
out = self.bn3(out)
if self.downsample is not None:
identity = self.downsample(x)
out += identity
out = self.relu(out)
return out
class ResNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(
self,
block,
layers,
num_classes=1000,
zero_init_residual: bool = False
):
super(ResNet, self).__init__()
self.inplanes = 64
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(3, self.inplanes, kernel_size=7, stride=2, padding=3,
bias=False)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(self.inplanes)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.maxpool = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1)
self.layer1 = self._make_layer(block, 64, layers[0])
self.layer2 = self._make_layer(block, 128, layers[1], stride=2)
self.layer3 = self._make_layer(block, 256, layers[2], stride=2)
self.layer4 = self._make_layer(block, 512, layers[3], stride=2)
self.avgpool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((1, 1))
self.fc = nn.Linear(512 * block.expansion, num_classes)
for m in self.modules():
if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
nn.init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight, mode='fan_out', nonlinearity='relu')
elif isinstance(m, (nn.BatchNorm2d)):
nn.init.constant_(m.weight, 1)
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
# Zero-initialize the last BN in each residual branch,
# so that the residual branch starts with zeros, and each residual block behaves like an identity.
# This improves the model by 0.2~0.3% according to https://arxiv.org/abs/1706.02677
if zero_init_residual:
for m in self.modules():
if isinstance(m, Bottleneck):
nn.init.constant_(m.bn3.weight, 0) # type: ignore[arg-type]
elif isinstance(m, BasicBlock):
nn.init.constant_(m.bn2.weight, 0) # type: ignore[arg-type]
def _make_layer(self, block, planes, blocks, stride=1):
downsample = None
if stride != 1 or self.inplanes != planes * block.expansion:
downsample = nn.Sequential(
conv1x1(self.inplanes, planes * block.expansion, stride),
nn.BatchNorm2d(planes * block.expansion),
)
layers = []
layers.append(block(self.inplanes, planes, stride, downsample))
self.inplanes = planes * block.expansion
for _ in range(1, blocks):
layers.append(block(self.inplanes, planes))
return nn.Sequential(*layers)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv1(x)
x = self.bn1(x)
x = self.relu(x)
x = self.maxpool(x)
x = self.layer1(x)
x = self.layer2(x)
x = self.layer3(x)
x = self.layer4(x)
x = self.avgpool(x)
# For `torch.flatten`, this blog may help: https://blog.csdn.net/GhostintheCode/article/details/102530451
# so `x = torch.flatten(x, 1)` is equivalent to `x = x.view(x.size(0), -1)` in the previous versions, where `x.size(0)` is the batch_size
x = torch.flatten(x, 1)
x = self.fc(x)
return x
def resnet18(pretrained=False, **kwargs):
"""Constructs a ResNet-18 model.
Args:
pretrained (bool): If True, returns a model pre-trained on ImageNet
"""
model = ResNet(BasicBlock, [2, 2, 2, 2], **kwargs)
if pretrained:
model.load_state_dict(model_zoo.load_url(model_urls['resnet18']))
return model
def resnet34(pretrained=False, **kwargs):
"""Constructs a ResNet-34 model.
Args:
pretrained (bool): If True, returns a model pre-trained on ImageNet
"""
model = ResNet(BasicBlock, [3, 4, 6, 3], **kwargs)
if pretrained:
model.load_state_dict(model_zoo.load_url(model_urls['resnet34']))
return model
def resnet50(pretrained=False, **kwargs):
"""Constructs a ResNet-50 model.
Args:
pretrained (bool): If True, returns a model pre-trained on ImageNet
"""
model = ResNet(Bottleneck, [3, 4, 6, 3], **kwargs)
if pretrained:
model.load_state_dict(model_zoo.load_url(model_urls['resnet50']))
return model
def resnet101(pretrained=False, **kwargs):
"""Constructs a ResNet-101 model.
Args:
pretrained (bool): If True, returns a model pre-trained on ImageNet
"""
model = ResNet(Bottleneck, [3, 4, 23, 3], **kwargs)
if pretrained:
model.load_state_dict(model_zoo.load_url(model_urls['resnet101']))
return model
def resnet152(pretrained=False, **kwargs):
"""Constructs a ResNet-152 model.
Args:
pretrained (bool): If True, returns a model pre-trained on ImageNet
"""
model = ResNet(Bottleneck, [3, 8, 36, 3], **kwargs)
if pretrained:
model.load_state_dict(model_zoo.load_url(model_urls['resnet152']))
return model
if __name__ == '__main__':
model = resnet18()
print(model)